Contents
What Is a Fuse Box?
A fuse box is the heart of a vehicle’s electrical system. It consists of one or more sites where all the wiring gathers, and it uses a variety of fuses and relays to keep things working properly. When all systems operate correctly, current flows from the battery through an individual fuse and to the electrical components.
Most fuses have two terminals, and the current flows via a small wire or piece of metal. When too much current flows through the fuse, that element breaks or melts, stopping dangerous current from flowing.
Suppose there is a malfunction, and a component fails. Or an electrical wire fails, allowing excessive current flow through the circuit. Either way, the fuse will disconnect the circuit, preventing overheating and a possible electrical fire.
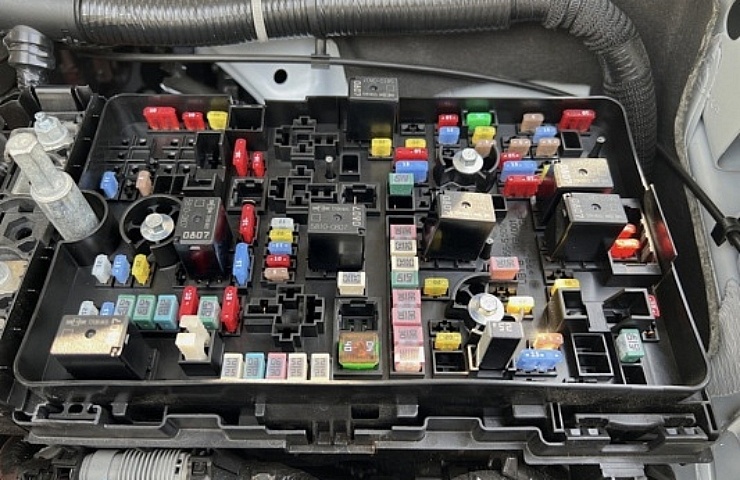
Instead of placing each fuse along the electrical circuits, automakers wisely gather all the fuses together in a fuse box. There’s usually one fuse box under the hood, and depending on the vehicle, there might be additional units in other locations.
Every carmaker places the fuse box in a different location. Cadillacs usually hide the fuse box under the rear seat. BMW and Mercedes-Benz vehicles position them in the trunk. Some even place a smaller fuse box in the passenger compartment. Older classic cars had fuses under the driver’s side dashboard, requiring a contortionist to access. Check your owner’s manual to verify your car’s specific fuse box locations.
Fuse Options
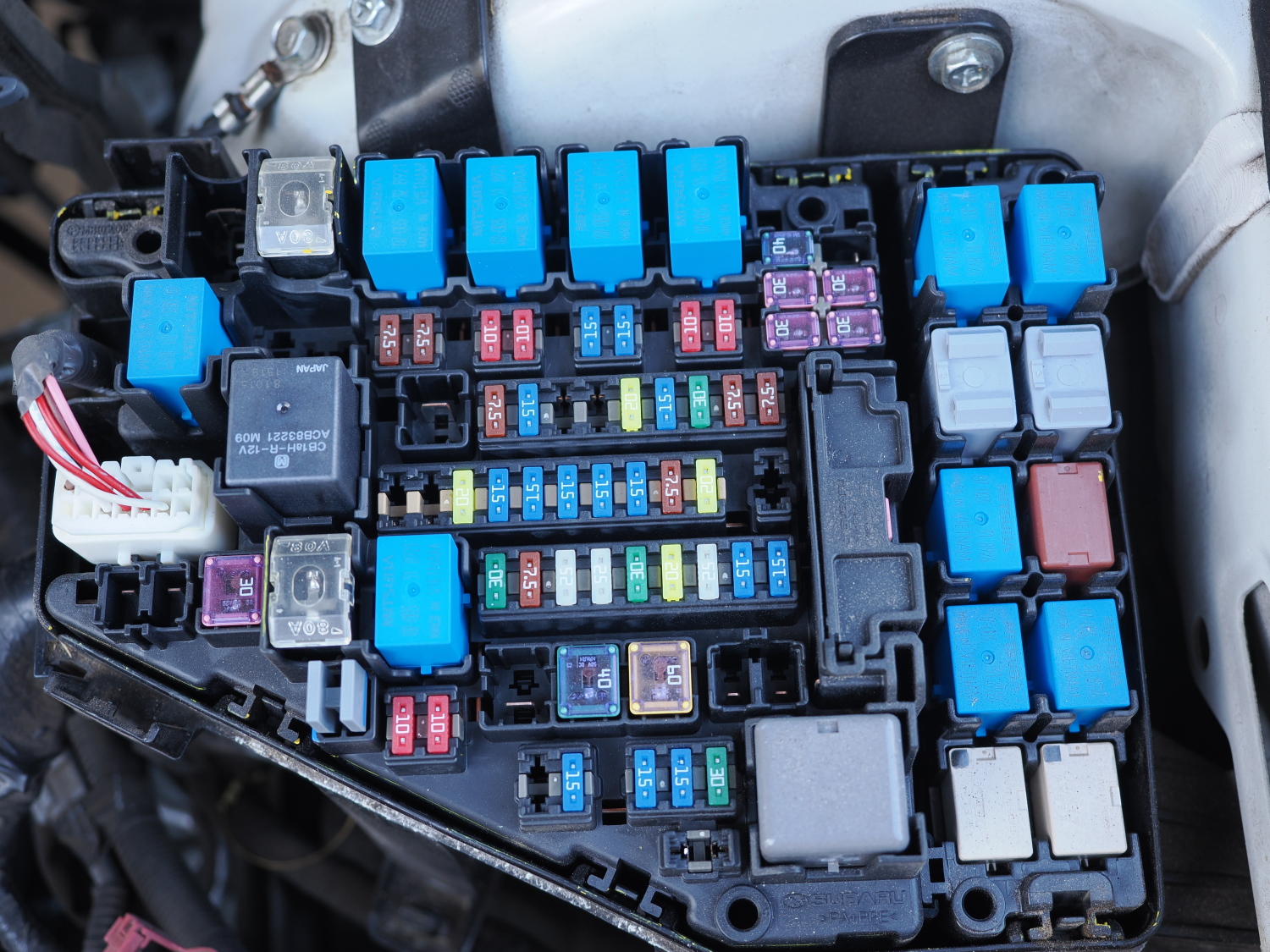
Most modern cars have blade (or spade) fuses in the fuse box. Automotive fuses are color-coded, easy to access, and easy to check. They consist of a plastic covering with two metal terminals. A thin piece of metal between the terminals acts as the fuse.
Fuses come in various sizes, from standard to mini and micro designations.
- Older cars have various fuse options, including glass cylinders (SFE fuses and AG fuses).
- Foreign cars might have Lucas fuses or torpedo-type fuses.
Again, check your owner’s manual to find what fuse type your car uses.
Shop now for automotive fusesInside the Fuse Box
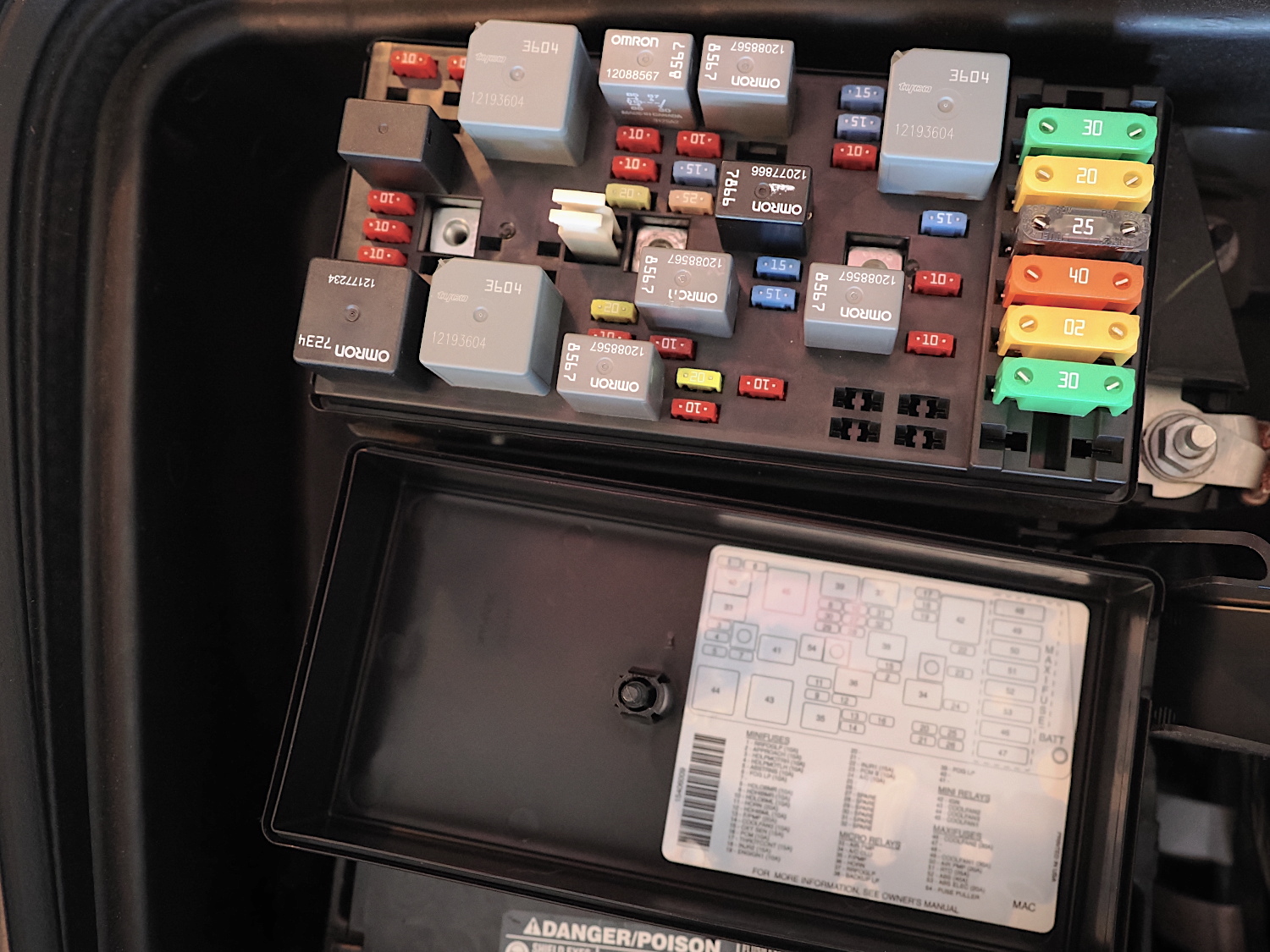
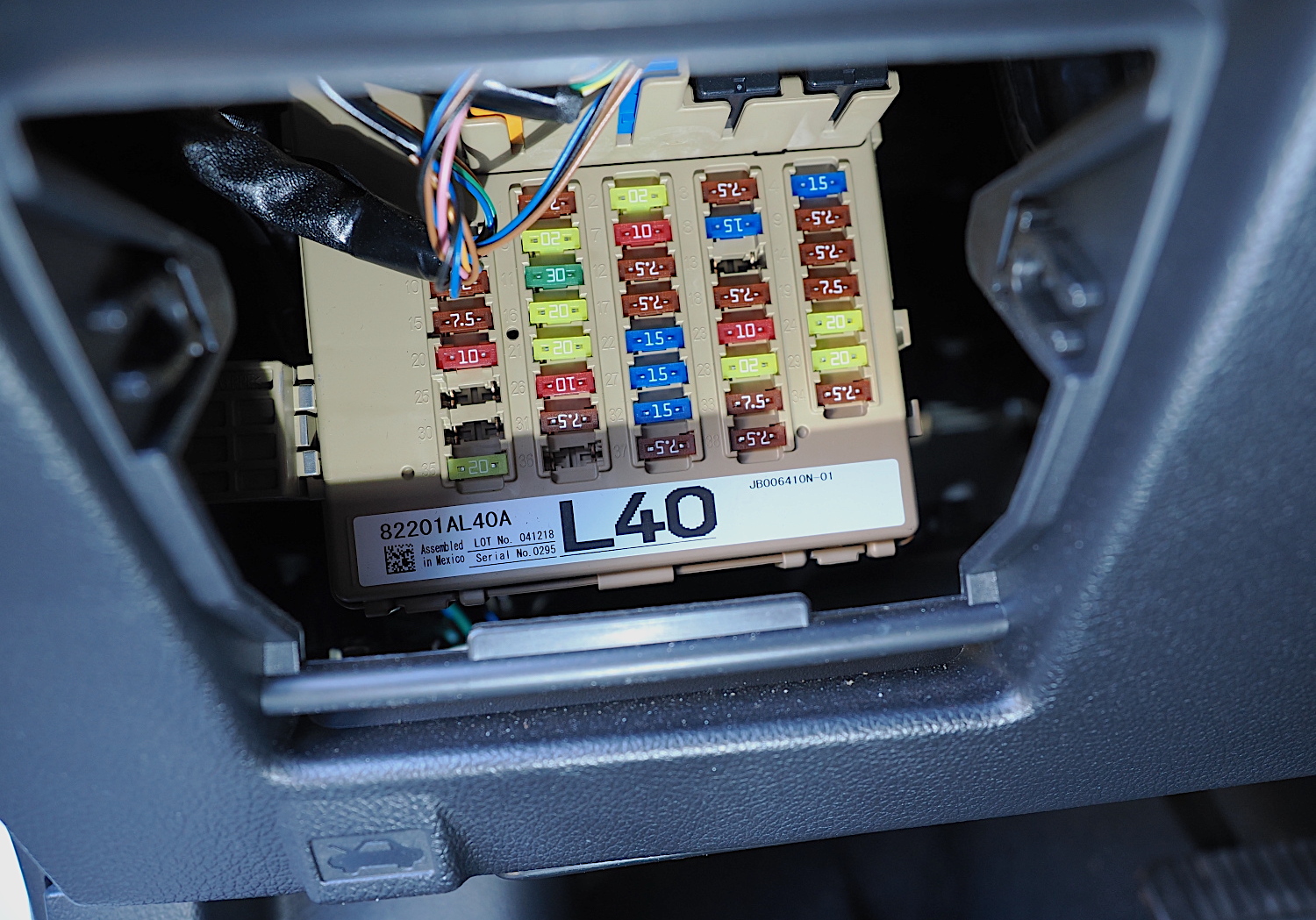
After you’ve located the fuse box in your car, you’ll need to loosen the clips or bolts that hold the covering in place. Inside, you should see rows of fuses.
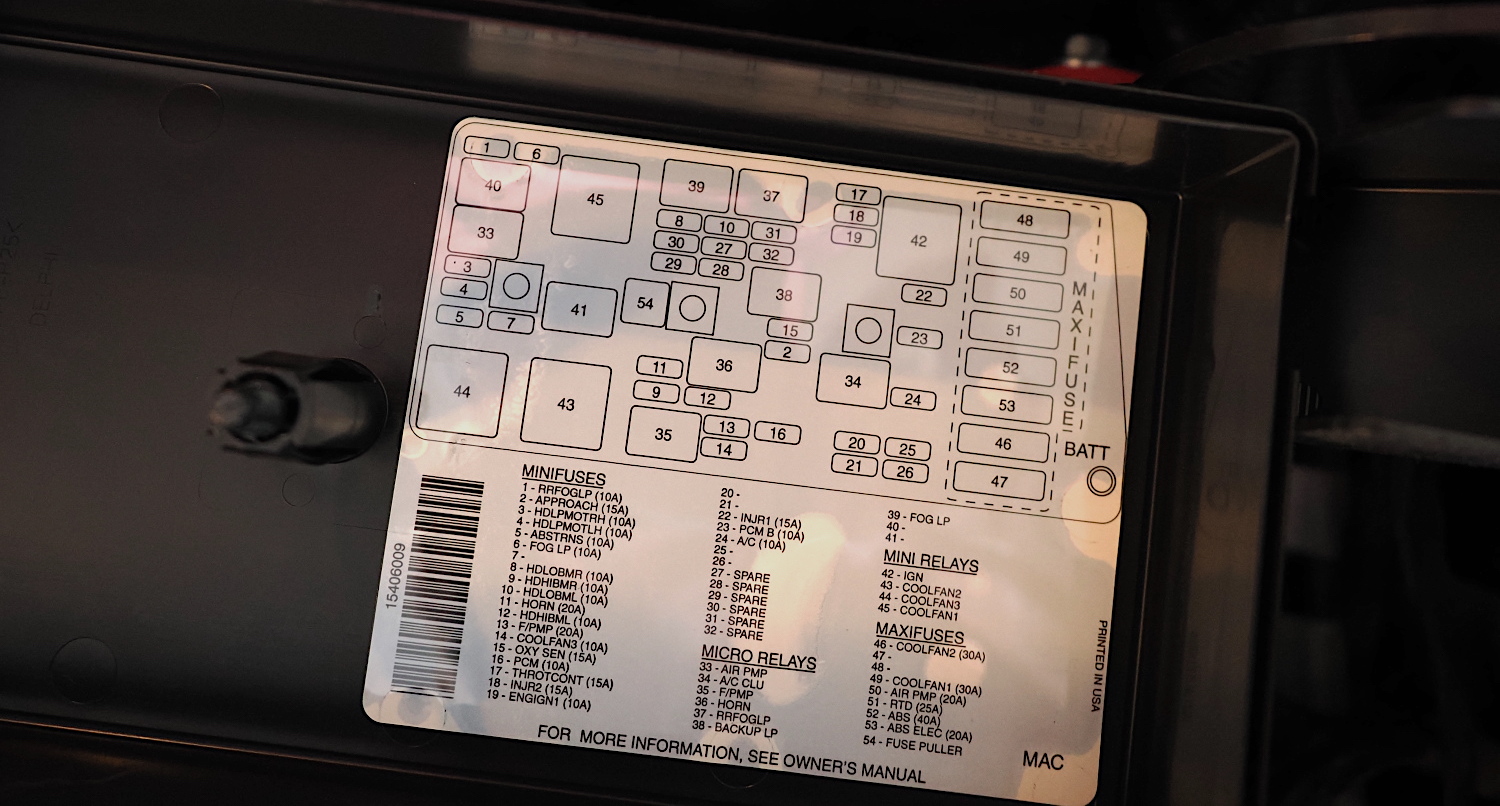
Fuses come in different amperage ratings depending on need, and they’re color-coded to indicate that amperage. The fuse box typically has a diagram on the bottom of the box lid to show which fuse is for which component. The owner’s manual also provides this information. Fuse boxes also usually include a plastic tool, similar to tweezers, to remove and replace fuses.
Don’t be alarmed if you see an empty slot in the fuse box. Usually, the manufacturer makes a “one size fits all” fuse box. If your car doesn’t include a specific circuit, then there’s no need for a fuse in that space.
Checking the Fuses
If an electrical component fails, a logical first step is to check the fuse for that device.
- Open the fuse box and locate the fuse indicated for the failed component.
- Use the provided tweezers or your fingers to pull the fuse straight out of the connectors. Sometimes, you need to wiggle the fuse slightly to free it.
- Look closely to determine if the link between the two terminals is broken. If so, the fuse “blew” to prevent the circuit from causing further damage.
If the fuse needs replacing, be sure to get its exact replacement. Some car manufacturers provide spare fuses as part of the fuse box. Otherwise, you can buy a set of fuses to have on hand.
If you replace a blown fuse, be sure also to replace that spare fuse. You’ll want a replacement ready the next time a fuse blows.
Do not replace a fuse that failed with one that has a higher rating. That would allow more current to flow through the circuit than it was designed for, which could cause damage or even a fire.
Shop now for automotive fusesIf a fuse keeps blowing, you should become an electronic investigator to determine the cause. Something is forcing the fuse to activate. A common cause is exposed metal in a length of wire, which can short. The electrical component involved in the circuit could also be malfunctioning, causing excessive current draw.
Read: Car Fuses and Fuse Boxes – Types, Amps, Wiring and Circuits
Relays
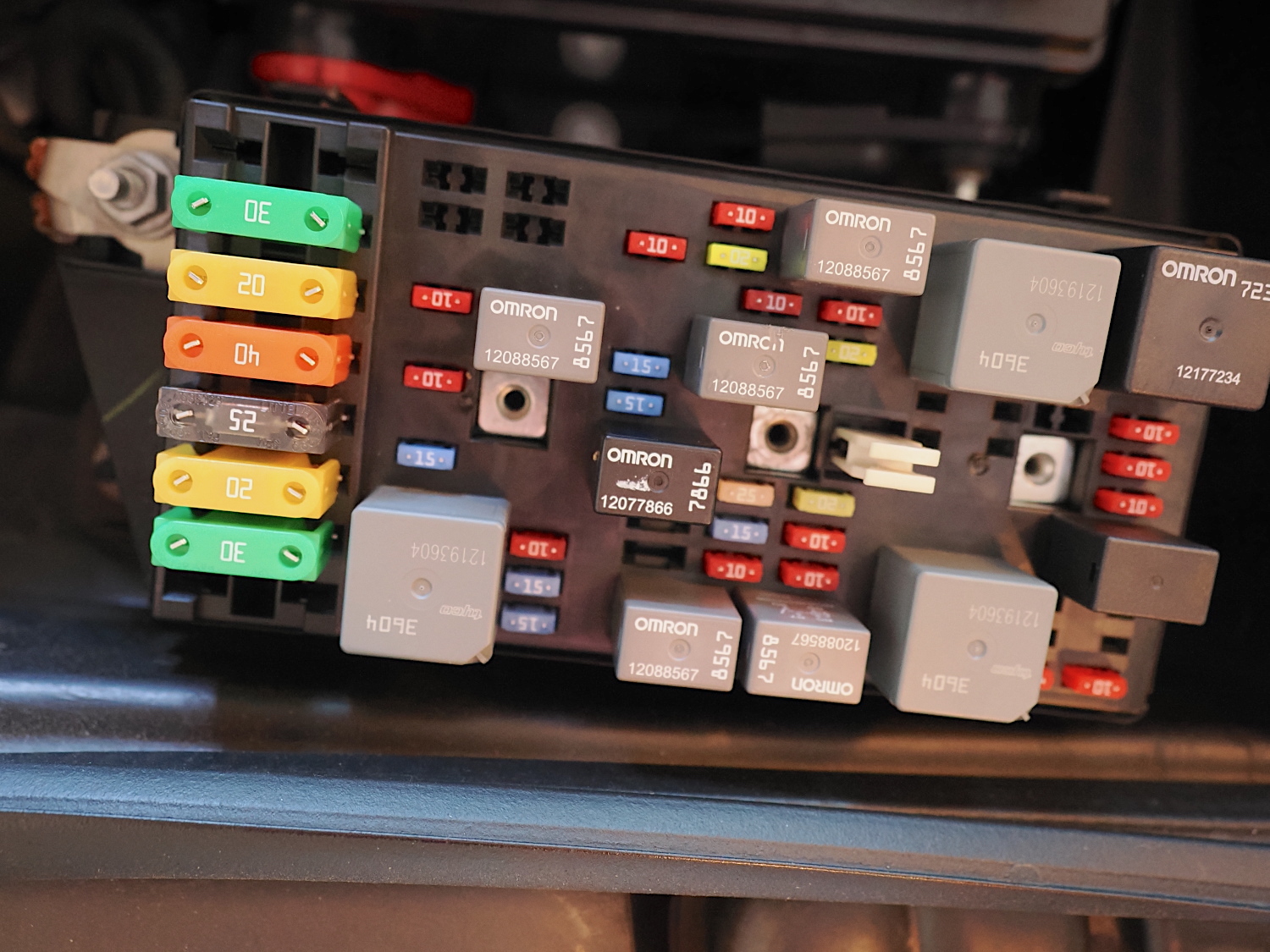
Besides the fuses, you’ll often find one or more cube-shaped devices in the compartment. Those are typically relays that allow high-amperage flow to electrical components. They, too, could be replaced if they fail, but they are not fuses. An automotive relay is more like a switch that allows the current to flow.
Replacing a Fuse Box
Individual fuses are the sacrificial lamb in an electronic circuit that saves the rest of the system. So, you would typically not need to replace an entire fuse box. This would be a labor-intensive project, as the wiring harnesses must be properly attached behind the fuse box. If it was part of an extensive electrical meltdown, of course you would need to replace the whole box.
For classic cars, the wiring has probably been hacked over the years. In that case, you might opt for a new wiring harness with a modern fuse box. This might be the only time you would choose to replace the fuse box.
Shop now for fuse boxesFuse boxes are a vital component of a vehicle’s electrical system. Fortunately, the box seldom causes issues. Instead, it’s a single fuse that blows. Thankfully, that’s easy to replace.


 Fuses come in various sizes, from standard to mini and micro designations.
Fuses come in various sizes, from standard to mini and micro designations.