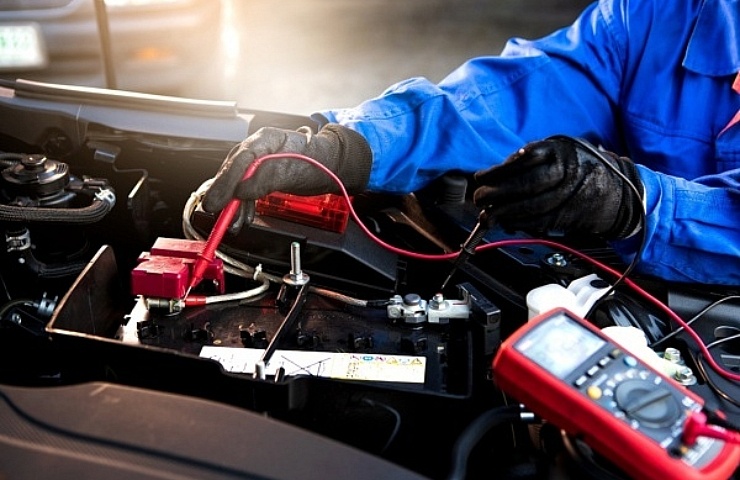
- If your car doesn’t start at all, the battery could be dead.
- If the car starts but then dies, the alternator may not be charging the battery.
Although, there are exceptions to these rules.
The Car Battery’s Purpose
A car battery provides the power your vehicle needs to start and keep running. When you start the vehicle, the battery sends power to the system’s ignition coil, starter, and other components.

Optima RedTop Car Battery
Most car batteries are known as SLI (starting, lighting, and ignition) batteries. There are six cells, each containing two plates or a grid. One plate is constructed of lead, while the other is made from lead dioxide. Each battery cell can produce approximately two volts of energy, which is why the average car battery is 12 volts.
Here’s how the battery starts your car:
- Your car has either a starter button or an ignition switch. This activates the starter relay.
- When you turn the key or push the button, a small current is sent to the starter relay.
- As the contacts close, the car battery sends voltage to the starter motor.
- The gears turn to start the car.
Even if the alternator isn’t functioning correctly, a fully charged car battery can keep the engine running for a short time.
Shop now for batteriesWhat Is an Alternator?
When the car runs, the alternator is responsible for recharging the battery. It also supplies power to the electrical components.

2004-2008 Ford F150 Alternator
The alternator is considered a generator. It turns rotational energy into electrical energy with the belt and pulley system. Here are an alternator’s components:
- Rotor and stator. These parts are responsible for producing electricity. The rotor is cylindrical with magnets surrounding it. It spins inside the stator, which is holding a fixed set of copper wiring. Electricity is created by magnets moving over the wiring.
- Voltage regulator. This regulator is responsible for supervising how much power is made by the alternator. It oversees the voltage level that’s output to the battery while delivering the remainder of the power to the vehicle’s electronics.
- Diode rectifier. This part converts the alternator’s voltage to recharge the battery.
- Cooling fan. Alternators get hot and must be cooled to work properly. The alternator is built with an aluminum casing and vents to release some of the heat, but the rotating fans add extra cooling. The newer alternators have internal cooling fans, while older models have external blades.
Symptoms of a Bad Battery
Car batteries are designed to last between three and five years. Driving short distances and operating a vehicle in extreme temperatures can shorten its life. With this short lifespan, you will likely deal with a dead car battery at some point.

Odyssey Extreme Car Battery
Here are the common warning signs of a dead car battery.
- A clicking sound while trying to start the vehicle
- Slow cranking situation— a “rurring” sound while trying to start the vehicle
- The “check battery” light is illuminated on the dashboard
- Dim or flickering lights
- Bloating or swelling of the battery case
- Cracked or damaged battery case
- Rotten egg smell from the battery
In some cases, there’s nothing wrong with the battery, but there is an issue with the connection. If you think you have a dead car battery, it’s wise to first clean the battery terminals with baking soda and water. You should also check the connections to ensure they are secure.
Additionally, some of these symptoms are also indicative of a bad starter. That’s why you want to perform a complete diagnosis before replacing the battery.
Shop now for batteriesSymptoms of a Bad Alternator
The lifespan of alternators is longer than that of batteries. Yet, water exposure, excessive heat, heavy loads, and faulty components can lead to premature failure. Once the alternator fails, the entire electrical load is left on the battery, which can’t sustain the demand for too long.

2010-2011 Toyota Camry Alternator
That’s why it’s essential to watch for these warning signs.
- Battery warning light on the dashboard
- Abnormal voltage readings on the dashboard gauge (when equipped)
- Continually dead battery
- Dim, flickering, or bright lights
- Malfunctioning or underpowered accessories, such as the radio, windows, and seat warmers
- Growling, grinding, or whining noises under the hood
- Burning rubber smell
As you can see, many of these symptoms resemble what happens when the car battery dies. Therefore, we recommend the following diagnostic steps to determine what’s wrong.
Shop now for alternatorsHow to Diagnose Whether the Problem Is the Battery or Alternator
There are two main ways to test the battery and alternator. You can use jumper cables or a jump starter. Check both with a voltmeter.

Autogage Battery Tester
Let’s start by examining what a jump starter might tell you.
- When the car doesn’t start, connect the jump starter or jumper cables.
- Allow the battery to charge, and try to start the engine again.
- If you can’t start the car, the battery may be too dead to jump.
- Once the car starts, remove the jumper cables.
- If the engine stalls, the alternator cannot keep the battery charged.
- If it doesn’t stall, but you continue having trouble starting the car, the battery is probably dying.
A more accurate diagnosis is made with a voltmeter or battery tester. Here are the steps to follow.
- Set the multimeter to DC voltage.
- Touch the red probe to the positive battery terminal (usually red or marked with a +).
- Touch the black probe to the negative battery terminal (usually black or marked with a -).
- If the reading has a minus in front of it (-12.6), you have the probes the opposite way.
The resting voltage should be no lower than 12.6 volts. A reading of 12.2 volts is 50% charged, while anything below 12 volts is discharged.
If the multimeter is less than 12.6 volts, charge the battery and test again. A battery that can’t hold a charge should be replaced.
Once the battery testing is complete, it’s time to move on to the alternator.
With the engine running, perform the same battery test as above.
If the alternator is charging the battery, you will see a reading between 13.8 and 14.4 volts. If the voltage is below that level, the alternator is undercharging the battery. Anything higher is overcharging, which is just as bad.
Shop now for battery testersHow Do You Replace the Battery?
If the battery is not holding a charge, it’s time for a replacement battery. Install the new battery by following these steps:
- Remove the old battery by disconnecting the cables, removing the negative cable first.
- Remove the battery bracket. It’s either a bracket held by two long bolts at the top of the battery or a clamp bolted on the bottom of the battery.
- Lift the battery out of the car. (Remember: it’s heavy.)
- Clean the battery connector to remove dirt and corrosion.
- Place the new battery back in its place and secure it with the bracket.
- Apply a thin layer of silicone dielectric grease on the battery terminals.
- Reconnect the battery, starting with the positive terminal first.
- Secure the connectors, but don’t overtighten.
With a battery memory saver tool, you don’t have to reprogram the seat settings, clock, or radio preset when disconnecting the battery.
Read this: A Battery Maintainer Saves Your Car’s Battery During Storage
Shop now for batteriesHow Do You Replace the Alternator?
You should also know how to replace the alternator. Here’s an overview of the process.
- Disconnect the battery, starting with the negative cable.
- Loosen the belt tensioner.
- Remove the serpentine belt.
- Remove the alternator’s wiring harness and connectors.
- Remove the alternator.
- Install the new alternator in its place. Align it with the bolt holes.
- Replace the belt.
- Ensure the tension is correct.
- Reconnect the battery.
- Retesting the system once you’ve replaced the parts is always good.
Get more details here: How to Test an Alternator (And Fix It!)
Shop now for alternators