Contents
What Is an Oxygen Sensor?
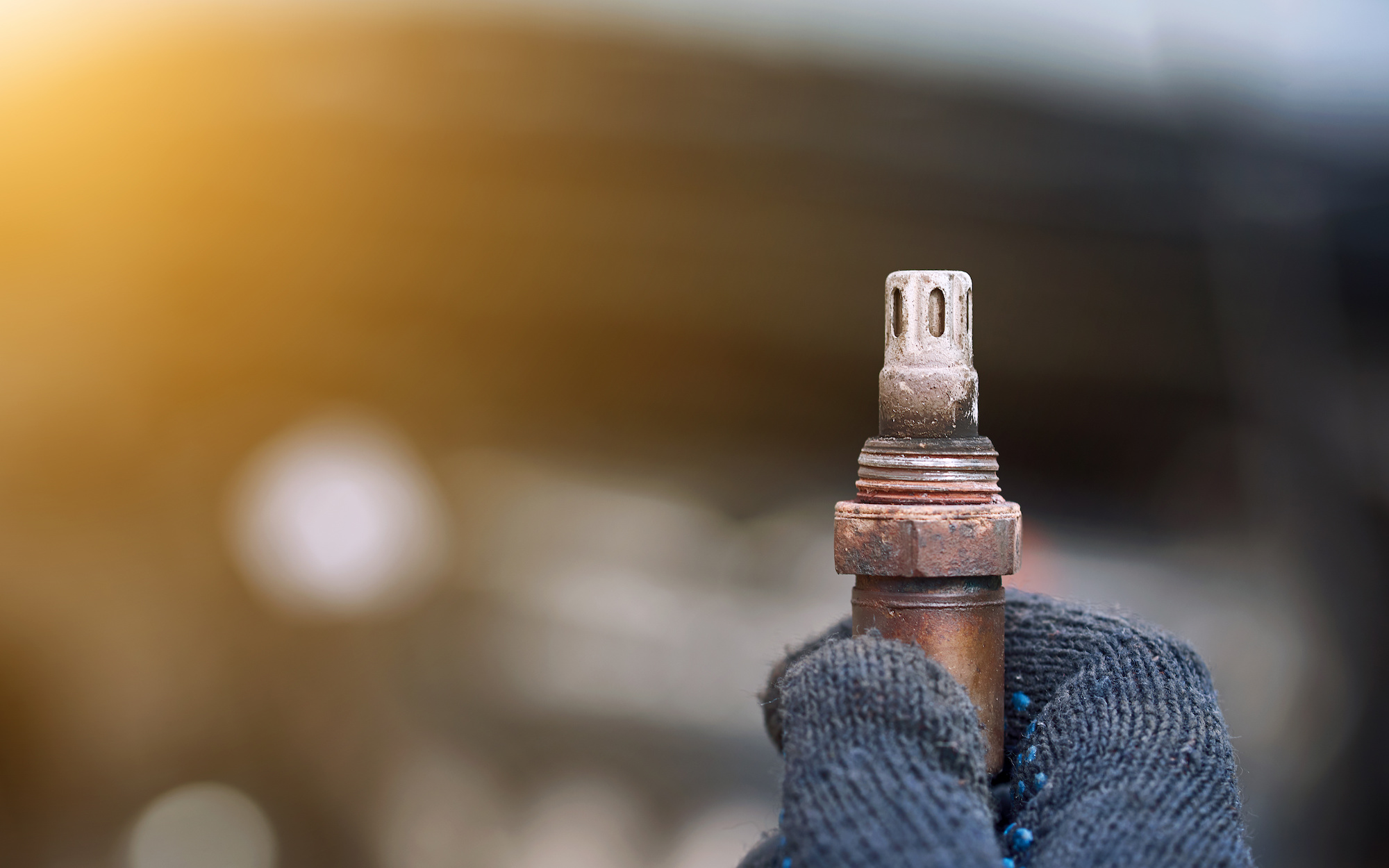
Oxygen sensors, also called O2 sensors, measure the amount of oxygen in a car’s exhaust. This helps reduce toxic emissions and ensures that your engine works optimally.
Gasoline engines combine air and fuel in a particular ratio.
- If oxygen is insufficient, the mixture is considered rich.
- If there’s too much oxygen, it’s considered lean.
- Both conditions can harm your engine.
Oxygen sensors detect how much air is present in the exhaust and direct the car’s computer, or ECU, to adjust the ratio accordingly by pumping more or less fuel into the engine.

While the O2 sensor before the cat helps measure the amount of unburned fuel, the one after monitors how well the catalytic converter is cleaning the exhaust. This second sensor also measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust, but only after the exhaust has passed through the cat.
Shop now for oxygen sensorsSigns That Your Oxygen Sensor Is Dirty
These are telltale signs that your O2 sensors are dirty:
- Poor fuel economy – Dirty O2 sensors will fail to detect how much air is in the engine, which causes them to send wrong or no information to the ECU. Because the ECU doesn’t know how much oxygen is in the engine, it may keep sending more fuel whether it’s needed or not. That means that your car might be using more fuel than usual.
- Exhaust fumes smell like gasoline – Because excess gasoline is pumped into the combustion chamber, it fails to burn completely. This unburned fuel finds its way out through the exhaust, hence the smell.
- Poor vehicle performance – Since the air-fuel mixture is not properly regulated, you may start experiencing slower acceleration, engine misfires, and even engine stalling.
The check engine light comes on – The check engine light will light up if it detects malfunctioning emissions components, including the O2 sensor. The tricky thing about the check engine light is that it can come on for many reasons. Make sure you perform a diagnosis with a scan tool to be certain that the O2 sensor is the issue.
Don’t Clean a Dirty Oxygen Sensor, Replace It
As exhaust flows constantly over the oxygen sensors in your car, it’s no surprise that over time contaminants can become lodged inside its sensitive components. While some sources suggest cleaning an oxygen sensor with carburetor cleaner or by soaking it in gasoline, we cannot recommend cleaning oxygen sensors. There are too many delicate electronic components that can be irreversibly damaged to make the effort worth the hassle.
If your oxygen sensor is dirty, it’s time to replace it. You’d have to remove the sensor anyhow to clean it, so the labor is the same. New sensors typically cost between $50 and $200 each.
First, gather these tools:
- WD-40 or other penetrating oil
- 22 mm or ⅞” open-end wrench or O2 sensor wrench
- Clean, soft cloth
- Safety gear: eyeglasses and gloves
- Jack and jack stands or ramps
Steps to Replace O2 Sensors
- Park on solid, level ground and place the car in park with the emergency brake activated. Allow the engine to cool off.
- Lift the car with a jack and support it with jack stands. Put on your gloves and eyewear.
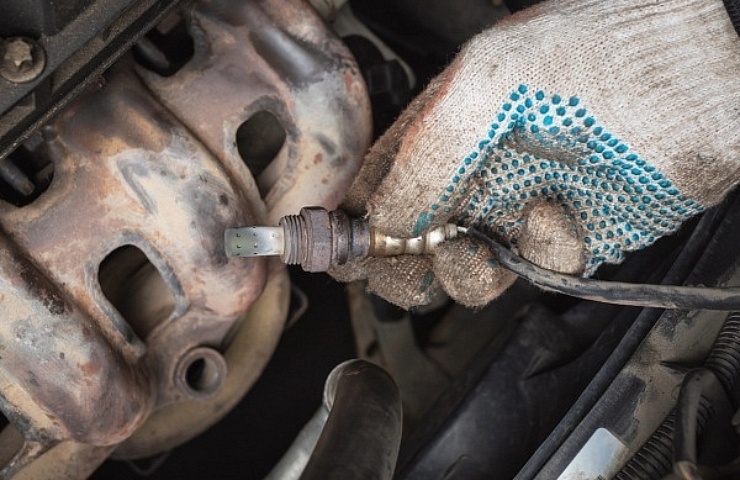
- The sensors are usually located near the end of the exhaust manifold but can be in other places, depending on your car model. Remember that most modern cars will have at least two sensors: one before the catalytic converter and one after.
- Evenly spray WD-40 or your preferred penetrating oil on each sensor and let it sit for 10 to 15 minutes. WD-40 and other penetrating oils will work their way into the sensor’s threads, making them easier to remove.
- Use a wrench to detach the sensors from the inlets. Carefully disconnect the wire connectors.
- Reinstall the new sensors in their original positions and tighten the bolts with a wrench. Carefully reconnect the wire connectors.
- Remove the jack and stands, then turn on your engine and see if the check engine light is on.
If dirty O2 sensors were the issue, replacing them should turn off the light. But if the check engine light remains illuminated, take a short drive or disconnect your negative battery terminal for about 15 minutes. Reconnect it and start your car again. If the problem was indeed dirty sensors, the light should disappear at this point. Replacement, rather than cleaning an oxygen sensor, is the way to go.
Shop now for oxygen sensors

 The check engine light comes on – The
The check engine light comes on – The