Contents
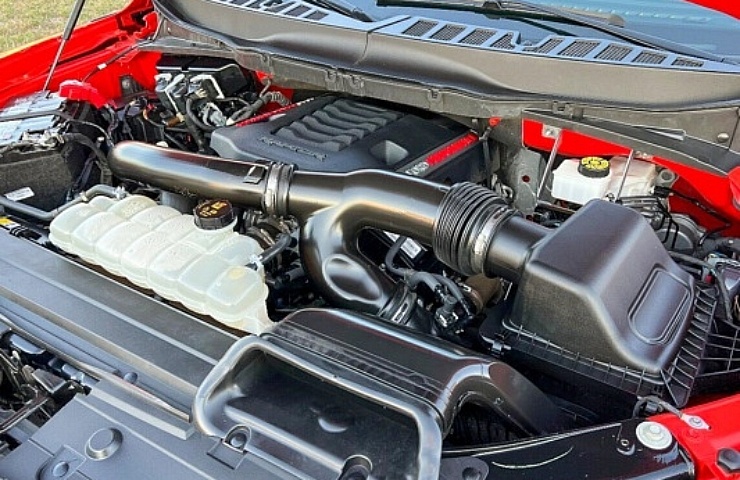
These somewhat common technologies, bundled and branded by Ford as “EcoBoost,” maximizes fuel efficiency while using turbocharging for additional power.
The name EcoBoost combines the words “ecological” and “boost.” The “eco” refers to being ecologically friendly, and the “boost” refers to the turbocharged boost for better acceleration, towing, and hauling a cargo load.
Today, there are more than 10 EcoBoost engines. They range from the powerful 450-horsepower twin-turbocharged 3.5-liter V-6 EcoBoost that powers the F-150 Raptor to the 1.5-liter 180-horsepower three-cylinder turbocharged EcoBoost in the Ford Escape crossover utility vehicle.
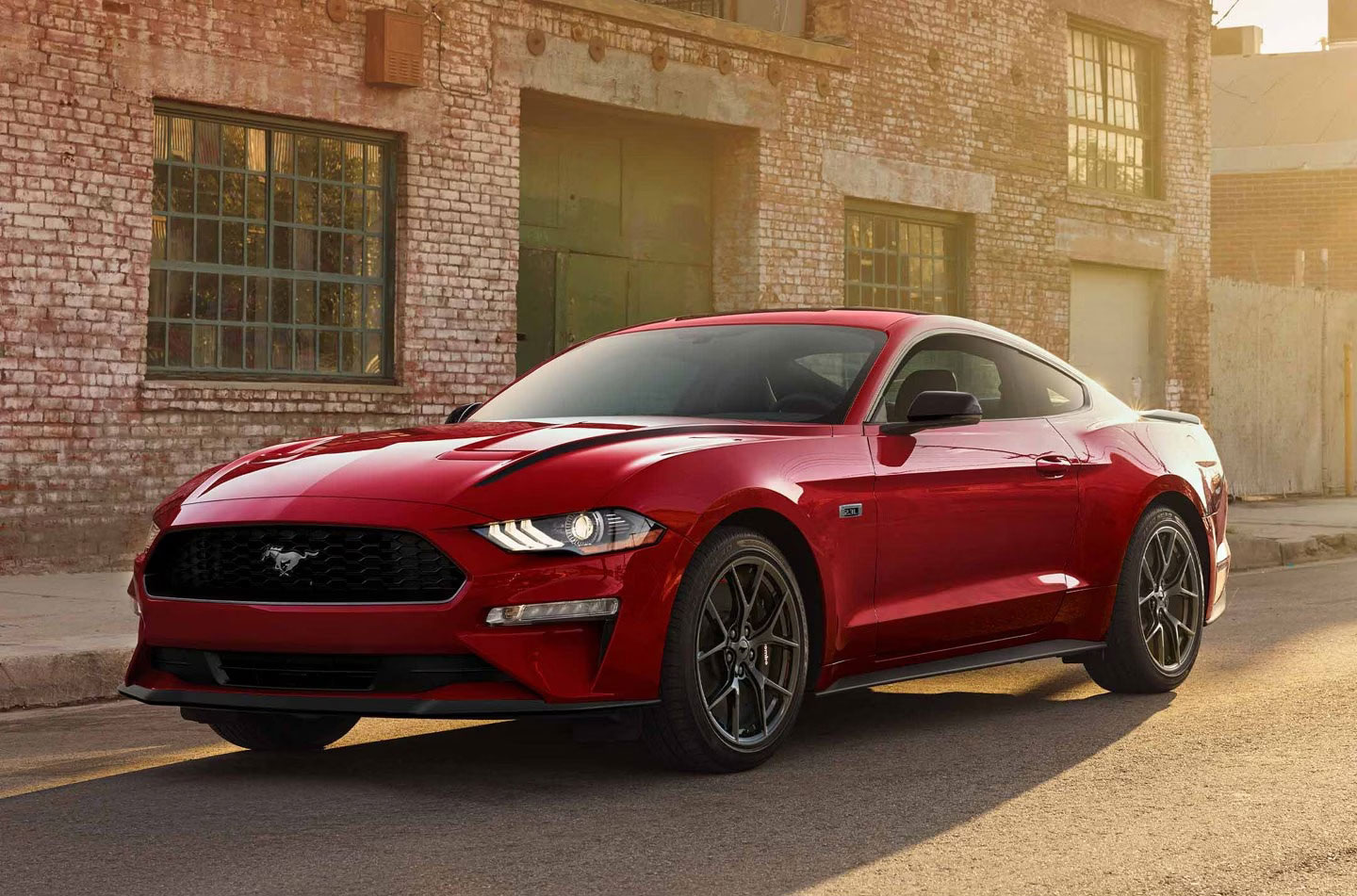

The Ford Mustang EcoBoost comes with a 2.3-liter turbocharged four-cylinder engine providing 310 horsepower and 350 pound-feet of torque.
EcoBoost is not the same as a hybrid powertrain, although some Ford hybrids use an EcoBoost engine. The term Ecoboost is applied only to the gasoline internal combustion engine only—not the system using a battery and electric motor.
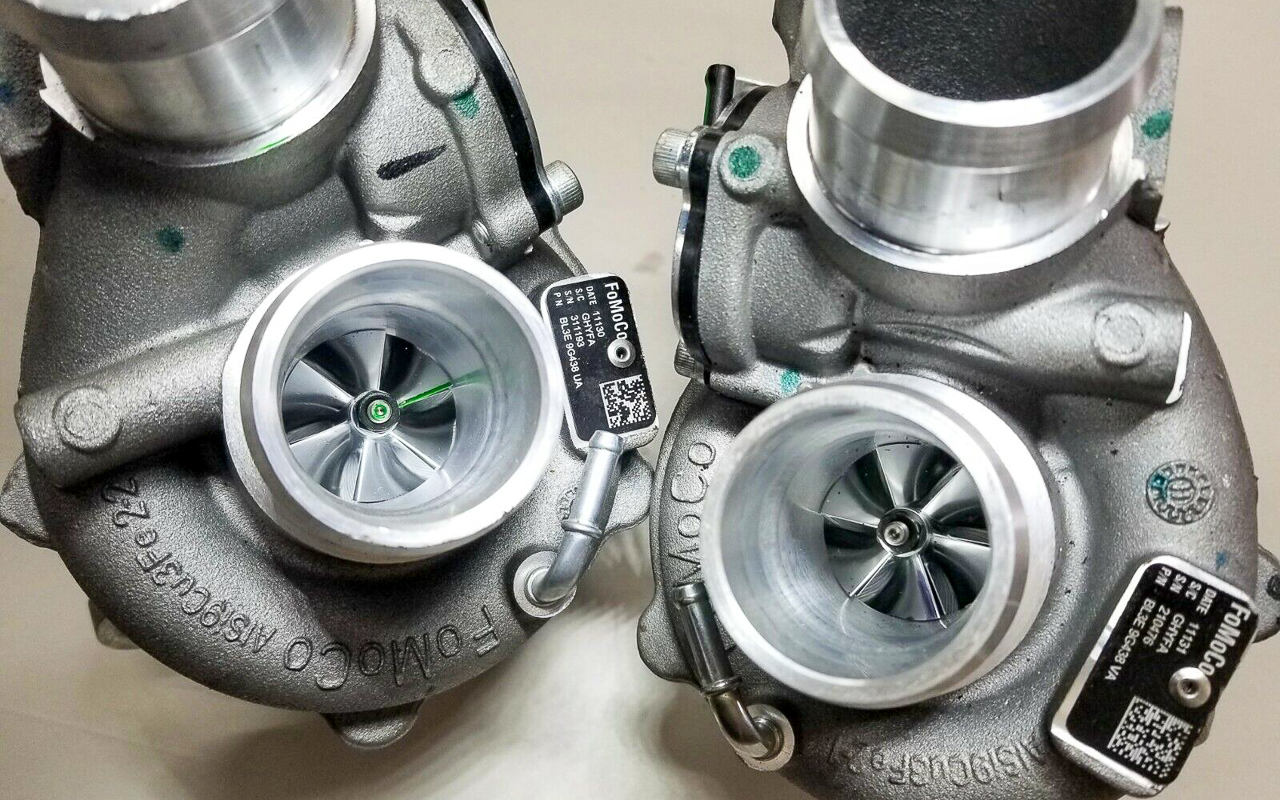

EcoBoost engines use turbochargers to boost horsepower and efficiency.
History of the EcoBoost Engine
Congress enacted corporate average fuel economy (CAFE) standards to reduce energy consumption by increasing the fuel economy of cars and light trucks. CAFE standards are fleet-wide averages that each automaker must achieve yearly. These standards are frequently raised over the years, reflecting the federal government’s increasing priority on improving overall fuel efficiency by utilizing energy efficient technologies.
Read: Groovy Ford Pinto Cruising Wagon Is Far Out
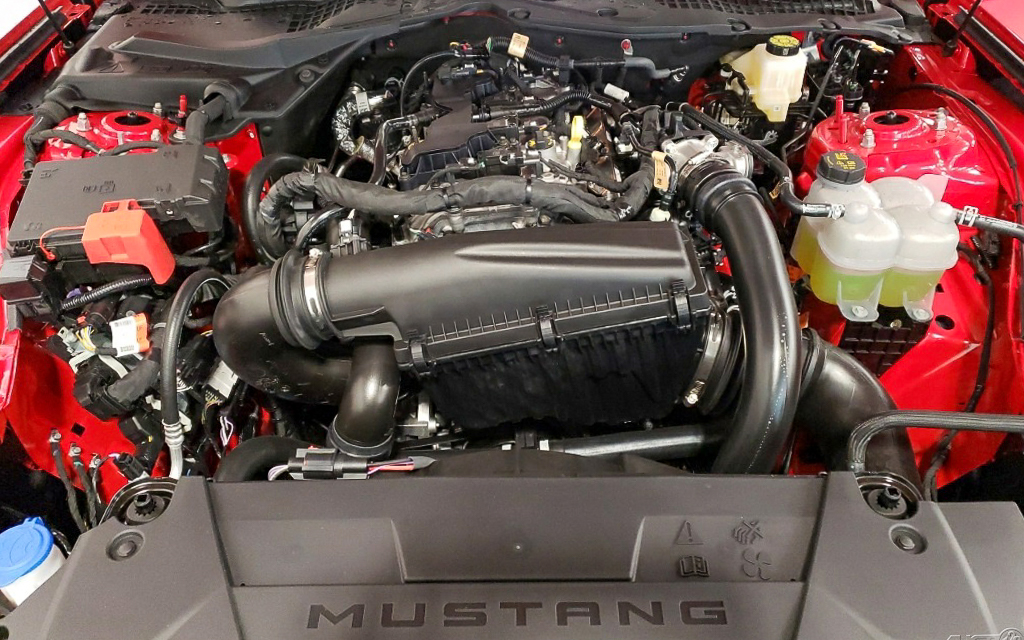

The 1974 Mustang 2.3-liter 4-cylinder engine made 88 hp. This 2024 Mustang 2.3L 4-cylinder EcoBoost engine makes 315 hp.
Ford’s EcoBoost technology helped the company meet CAFE standards with smaller engines while still offering high performance to consumers. In its development, Ford initially partnered with FEV Inc., a global mobility company.
An EcoBoost engine, according to Ford, offers up to 20 percent better fuel economy and additional horsepower—while reducing harmful greenhouse emissions by up to 15 percent.
EcoBoost was launched in 2009 in a 2010 Ford Taurus SHO with a 3.5-liter V-6 engine. The 2009 launch also included a 1.0-liter and a 1.6-liter version of the new engine. That year, 14,439 EcoBoost engines were produced.
Shop now for Ford cars and trucksPros and Cons of the EcoBoost Engine
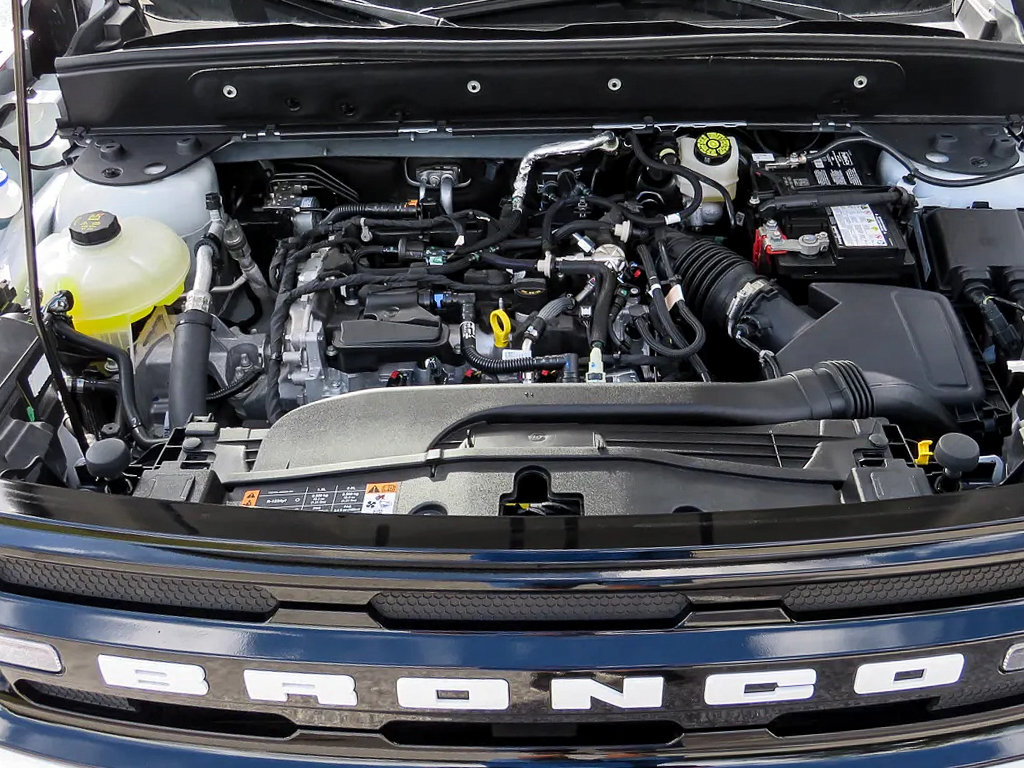

This Bronco Sport is powered by a 1.5-Liter EcoBoost 3-cylinder engine.
All gasoline-powered Ford vehicle models for 2024 are available with at least one choice of an EcoBoost engine, either as the standard engine or as an option.
Pros:
- Produces more horsepower
- Capable of towing more weight
- Less expensive than a hybrid option
- Fewer harmful tailpipe emissions
- Wide range of EcoBoost engine sizes to choose
Cons:
- Premium price when purchasing new
- Less fuel efficient than a hybrid
- More frequent maintenance than a conventional engine
- Some twin-turbocharger “whining” sound
Eco Mode vs. EcoBoost
While they sound similar, Eco mode and EcoBoost are entirely different. Vehicles with various drive mode settings have an Eco setting choice, along with Sport, Snow and Ice, and Normal. Selecting Eco mode simply reduces the engine’s performance output or changes transmission shift points to a lower rpm. This results in slower acceleration and less power when passing but better fuel economy and fewer greenhouse gas emissions.
On the other hand, EcoBoost is a type of Ford engine created to increase horsepower and reduce emissions regardless of driver settings.
Shop now for emissions and exhaust parts